Learning how to meditate for anger management offers a powerful approach to achieving emotional balance and inner peace. By incorporating meditation practices into daily routines, individuals can develop effective tools to control impulsive reactions and foster a calmer mindset. This guide explores various techniques and strategies to harness meditation as a means of managing anger constructively and promoting overall mental well-being.
From creating a conducive environment to practicing guided meditations and mindfulness exercises, this comprehensive overview provides practical steps for integrating meditation into your anger management plan. Embracing these practices can lead to reduced stress, enhanced self-awareness, and a more peaceful life even amid challenging circumstances.
Introduction to Meditation for Anger Management

Meditation serves as a powerful tool in managing anger by fostering greater emotional awareness and promoting calmness amidst stressful situations. It provides individuals with practical techniques to pause, reflect, and regulate their emotional responses, thereby reducing the likelihood of impulsive reactions that can have negative consequences in personal and professional relationships.
Engaging in meditation regularly offers numerous mental health benefits, including decreased stress levels, improved concentration, and enhanced emotional resilience. These practices help individuals develop a mindful approach to their emotions, enabling them to observe feelings of anger without immediate reaction. Over time, this cultivated awareness can significantly diminish the intensity and frequency of anger episodes, leading to more constructive and controlled responses.
Benefits of Meditation for Mental Health and Stress Reduction
Consistent meditation practice contributes to a healthier mental state by calming the nervous system and fostering a sense of inner peace. It reduces the production of stress hormones such as cortisol, which are often elevated during episodes of anger and anxiety. Additionally, meditation encourages a balanced perspective, helping individuals to interpret challenging situations more rationally and respond thoughtfully rather than impulsively.
Research indicates that meditation can improve mood, decrease symptoms of anxiety and depression, and enhance overall emotional stability. In the context of anger management, these benefits translate into better control over emotional triggers, improved patience, and a more compassionate attitude towards oneself and others.
Step-by-Step Overview of How Meditation Assists in Managing Anger Episodes
Understanding the process through which meditation aids in anger management can empower individuals to incorporate these practices effectively into their daily routines. The following steps Artikel how meditation can be used as a strategic approach to diffuse anger and promote emotional regulation:
- Recognize Early Signs of Anger: Before anger escalates, mindfully observe physical sensations, thoughts, or feelings that signal rising tension. Awareness is the first step to intervention.
- Pause and Breathe Deeply: Take a few slow, deep breaths. Focused breathing helps calm the nervous system and creates a mental space between stimulus and response.
- Engage in Mindful Observation: Turn attention inward to observe the emotion without judgment. Acknowledge the anger as a temporary state rather than a defining characteristic.
- Use Guided Meditation Techniques: Employ specific meditation practices such as body scans, loving-kindness meditation, or focused breathing to redirect attention and dissolve anger’s intensity.
- Develop a Calm Response: After calming the mind, choose a constructive response to the situation, whether it involves addressing the issue calmly or temporarily stepping away to prevent escalation.
Incorporating these steps consistently allows individuals to create a mental framework that reduces impulsivity, enhances emotional resilience, and fosters a more peaceful state of mind, especially when confronted with anger-provoking circumstances.
Preparing for Meditation Sessions
Establishing the right environment and mindset is essential for effective meditation, especially when managing anger. Proper preparation helps to create a calm and focused atmosphere, allowing the individual to fully engage in the practice and experience its benefits. Developing consistent routines around meditation also enhances its effectiveness in reducing emotional volatility.Creating an optimal setting and choosing suitable times for meditation can significantly influence the success of the practice.
Additionally, engaging in relaxation techniques before starting can help transition into a meditative state, making the session more productive and soothing.
Ideal Environment Setup for Effective Meditation
A conducive environment is fundamental for meditation, as it minimizes distractions and promotes mental clarity. The space should be quiet, comfortable, and free from interruptions. Natural light or soft, calming lighting can enhance relaxation, while clutter-free surroundings help maintain focus.To establish an effective meditation environment:
- Choose a spot with minimal noise, possibly away from busy areas or noisy appliances.
- Ensure the temperature is comfortable—neither too hot nor too cold—to prevent discomfort.
- Use calming elements such as soft cushions, a meditation mat, or a comfortable chair.
- Avoid electronic devices or keep them in silent mode to prevent disruptions.
- Optional: Incorporate calming scents like lavender or chamomile to enhance tranquility.
A consistent space dedicated solely to meditation encourages the mind to associate that environment with calmness and focus, which can deepen the effectiveness of anger management practices over time.
Selecting Appropriate Meditation Times
Timing plays a crucial role in maximizing the benefits of meditation. Identifying periods when the mind is naturally calmer can facilitate deeper relaxation and mindfulness. The goal is to choose times that align with one’s daily rhythm and minimize external stressors.Effective methods for selecting meditation times include:
- Practicing early in the morning before daily activities commence, when the mind is relatively fresh and less cluttered by worries.
- Scheduling sessions during mid-morning or late afternoon when emotional fluctuations, such as irritability or fatigue, are typically lower.
- Consistently meditating at the same time each day to build a routine and signal to the mind that it is time to relax.
- Considering periods of natural calmness, such as after a warm bath or gentle exercise, to enhance relaxation.
Aligning meditation with natural energy levels ensures that the practice is more effective, especially in managing anger, by fostering a sense of control and emotional balance throughout the day.
Relaxation Techniques to Prepare the Body and Mind
Before beginning meditation, engaging in relaxation techniques can ease physical tension and mental clutter, making it easier to enter a calm state. These practices help signal to the nervous system that it is time to unwind, facilitating a smoother transition into meditation.Some effective relaxation methods include:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Inhale slowly through the nose, hold for a few seconds, then exhale gradually through the mouth or nose. Repeating this process calms the nervous system and reduces immediate feelings of agitation.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense specific muscle groups for a few seconds, then release, working from the toes upward. This enhances body awareness and alleviates physical tension associated with anger.
- Mindful Body Scan: Systematically focus attention on different body parts, noticing sensations without judgment. This enhances present-moment awareness and diminishes emotional reactivity.
- Visualization Techniques: Imagine a peaceful place or scenario, such as a quiet forest or a calm lake, to evoke feelings of serenity and detachment from stressors.
Implementing these techniques prior to meditation not only prepares the body and mind but also establishes a routine that can lead to more profound emotional regulation, particularly in response to anger triggers.
Techniques and Methods for Meditative Anger Management

Effective anger management through meditation involves the application of various techniques tailored to promote calmness, self-awareness, and emotional regulation. Selecting appropriate methods can significantly enhance an individual’s ability to cope with anger swiftly and sustainably, fostering a more composed response to challenging situations.
Different meditation styles offer unique benefits suited to managing anger. Some focus on cultivating mindfulness and present-moment awareness, while others utilize visualization and controlled breathing to reduce immediate tension. Understanding these methods enables individuals to incorporate the most suitable practices into their daily routines for optimal emotional balance.
Specific Meditation Styles Suitable for Anger Control
- Mindfulness Meditation: Encourages non-judgmental awareness of thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations, helping individuals observe anger triggers without reacting impulsively.
- Guided Imagery: Uses visualization techniques to create calming mental images, promoting relaxation and emotional detachment from anger-provoking stimuli.
- Breathing Exercises: Focuses on controlled breathing patterns to activate the body’s relaxation response and reduce immediate emotional arousal.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Involves systematically tensing and relaxing muscle groups to alleviate physical tension associated with anger.
- Loving-kindness Meditation: Cultivates feelings of compassion and empathy, which can diminish hostile emotions and foster positive interactions.
Comparison of Meditation Techniques for Anger Management
| Technique | Typical Duration | Focus Area | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mindfulness Meditation | 10-30 minutes | Present-moment awareness of thoughts and feelings | Enhanced emotional regulation and awareness |
| Guided Imagery | 10-20 minutes | Visualization of calming scenes | Immediate relaxation and stress reduction |
| Breathing Exercises | 5-15 minutes | Controlled respiration patterns | Calms physiological response to anger |
| Progressive Muscle Relaxation | 15-30 minutes | Muscle groups from head to toe | Physical tension relief and emotional calmness |
| Loving-kindness Meditation | 10-20 minutes | Recitation of kind phrases | Reduces hostility and fosters compassion |
Deep Breathing Exercises to Calm Immediate Anger Responses
Deep breathing serves as a quick and effective method to manage acute anger episodes. It helps activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which counteracts the stress response and promotes relaxation.
- Find a comfortable seated position with your back straight and shoulders relaxed.
- Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen to monitor your breathing pattern.
- Inhale slowly through your nose, counting to four, ensuring your abdomen rises more than your chest.
- Hold your breath gently for a count of four.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth or nose for a count of six, feeling your abdomen fall.
- Repeat this cycle for 3-5 minutes, focusing solely on your breath to divert attention from anger triggers.
Proper breathing involves deep, diaphragmatic inhalations and controlled exhalations, which help regulate emotional responses and induce a state of calm.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation for Reducing Tension
This technique systematically relaxes muscle groups to diminish physical tension, often associated with anger. Regular practice enhances body awareness and the ability to release stress physically, leading to better emotional control.
- Begin by sitting or lying down in a quiet, comfortable environment.
- Close your eyes and take a few deep breaths to center yourself.
- Start with your feet: tense the muscles tightly by curling your toes or pressing your heels into the ground, hold for about five seconds.
- Release the tension suddenly and completely, noticing the sensation of relaxation.
- Move to your calves, thighs, abdomen, chest, arms, shoulders, neck, and face, repeating the tensing and relaxing process for each group.
- Pay close attention to the contrast between tension and relaxation, cultivating awareness of physical states.
- Finish the session by taking a few deep breaths and gently stretching if necessary.
This method helps reduce the physical manifestations of anger, allowing the mind to follow and maintain a calmer emotional state.
Guided Meditation Practices for Anger Relief
Guided meditation serves as a powerful tool in managing and alleviating anger by providing structured pathways for relaxation, self-awareness, and emotional regulation. These practices help individuals redirect intense feelings, promote calmness, and develop a healthier response to anger-provoking stimuli. Implementing guided meditations consistently can foster a sense of inner peace and resilience during challenging moments.
Effective guided meditations for anger relief incorporate visualization, body awareness, and affirmations. They serve as accessible methods for individuals to reconnect with their calm center, reframe negative emotions, and cultivate compassion towards themselves and others. Below are detailed scripts and techniques designed to maximize the benefits of meditation in anger management.
Guided Visualization for Releasing Anger
This visualization exercise helps individuals consciously release accumulated anger by imagining it as a tangible substance that can be safely let go. Through vivid imagery, participants learn to observe their emotions without judgment and create a mental space for healing.
Begin by finding a comfortable seated or lying position. Close your eyes gently and take a few deep breaths, inhaling calmness and exhaling tension. Visualize a situation or feeling that has triggered your anger. Imagine this anger as a dark, smoky cloud within your chest, growing heavier with each breath.
As you breathe out, picture this cloud slowly dissolving, dispersing into the air as a shimmering light or gentle mist. Feel the sensation of releasing this burden, allowing it to drift away effortlessly. Repeat this visualization several times, reinforcing your capacity to let go of anger and welcome peace into your heart.
Body Scan Meditation Focused on Tension Areas
Body scan meditation is an effective method for identifying and reducing physical tension associated with anger. By systematically bringing awareness to different areas of the body, individuals can release pent-up energy and promote relaxation.
- Start by assuming a comfortable position, closing your eyes, and taking slow, deep breaths to center yourself.
- Bring your attention to your feet. Notice any sensations, tightness, or discomfort. Allow these feelings to soften and dissolve as you exhale.
- Gradually shift your focus upward to your ankles, calves, knees, and thighs, observing any tension held in these areas. Use your breath to ease out tightness.
- Continue moving focus to your abdomen, chest, shoulders, arms, neck, and finally your face. With each region, consciously relax muscles and release any lingering anger-related tension.
- Conclude by visualizing a wave of warm, calming energy flowing through your entire body, leaving you feeling balanced and serene.
Incorporating Affirmations During Meditation
Affirmations are powerful statements that reinforce positive beliefs and emotional states. When integrated into meditation, they help reprogram the subconscious mind, foster calmness, and diminish anger’s grip.
- Choose affirmations that resonate personally, such as “I am calm and in control,” “I release all anger,” or “Peace flows through me.”
- Repeat these affirmations silently or aloud during meditation sessions, especially during moments of stillness or after visualization exercises.
- Combine affirmations with deep breathing, synchronizing each statement with an inhalation or exhalation for enhanced effect.
- Use affirmations consistently to build a habit, gradually replacing negative thought patterns associated with anger with positive, calming beliefs.
Effective affirmation example: “With each breath, I let go of anger and welcome peace and understanding into my heart.”
Incorporating Mindfulness and Self-awareness
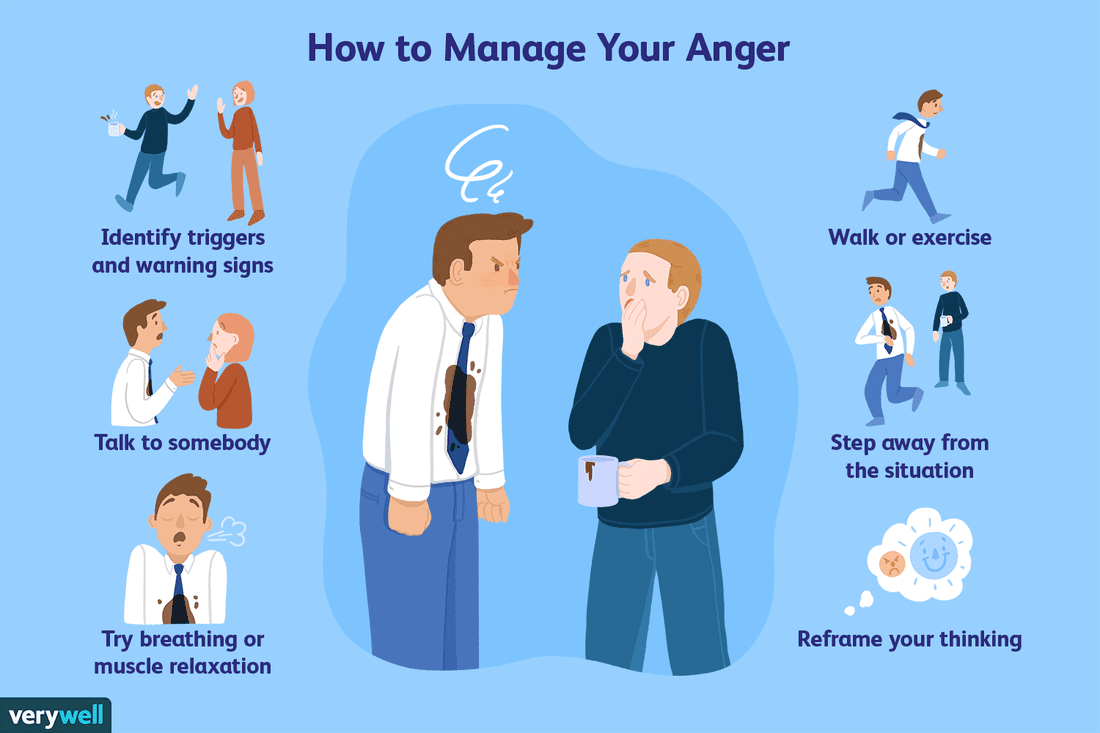
Developing mindfulness and self-awareness is essential for effectively managing anger. By integrating these practices into daily routines, individuals can better identify early signs of emotional escalation and respond constructively before anger intensifies. These techniques foster a deeper understanding of personal emotional triggers, promoting a calmer and more balanced demeanor in various situations.Mindfulness and self-awareness serve as foundational components in maintaining emotional regulation.
Regular practice enhances one’s ability to notice subtle changes in thought, feeling, and bodily sensations that signal rising anger. This awareness allows for timely intervention, reducing the likelihood of reactive outbursts and promoting healthier interpersonal interactions.
Integrating Mindfulness Techniques into Daily Routines
Embedding mindful practices into everyday activities creates a consistent foundation for anger management. This approach involves intentionally dedicating moments throughout the day to observe and accept present experiences without judgment. Consider the following methods:
- Mindful Breathing: Incorporate short breathing exercises during routine activities such as commuting, working, or waiting in line. Focus on slow, deep breaths, paying attention to the sensation of air entering and leaving the body. This simple practice helps anchor awareness and reduces emotional reactivity.
- Mindful Eating: Pay full attention to the taste, texture, and aroma of meals. Eating slowly and savoring each bite fosters grounding and promotes calmness, diminishing emotional triggers associated with hurried or distracted eating.
- Scheduled Mindfulness Breaks: Set aside specific times during the day—such as mid-morning or late afternoon—for brief mindfulness sessions, perhaps as short as five minutes. During these moments, focus solely on the present moment using breathing or sensory observations, cultivating ongoing self-awareness.
Sensory Awareness Exercises for Recognizing Early Signs of Anger
Detecting the initial onset of anger is crucial for preemptive action. Sensory awareness exercises sharpen the ability to notice subtle physical and emotional cues that signal escalating frustration or irritation.Implement these exercises:
- Body Scan Meditation: Periodically, pause and scan the body from head to toe, paying close attention to areas commonly associated with tension, such as shoulders, jaw, or stomach. Recognizing physical signs like clenched fists or tightness allows for early intervention.
- Emotion and Sensation Journaling: Maintain a journal where you record specific instances of emotional shifts. Note physical sensations, thoughts, and external triggers present at the moment. Over time, this practice reveals patterns and early indicators of anger.
- Sensory Grounding Techniques: Engage your senses by focusing on five things you see, four you hear, three you feel (touch), two you smell, and one you taste. This grounding diversifies awareness and helps shift focus away from escalating emotions.
Journaling Experiences and Emotions for Ongoing Self-awareness
Post-meditation journaling is a valuable tool for cultivating ongoing self-awareness. It encourages reflection on emotional responses, triggers, and progress over time. Documenting these experiences deepens understanding and supports tailored strategies for anger management.Some effective practices include:
- Emotion Tracking: After each meditation session, write about the emotions experienced, their intensity, and any physical sensations. Note how these feelings fluctuate and what thoughts accompany them.
- Trigger Analysis: Identify situations or interactions that triggered heightened emotions. Reflect on how mindfulness influenced your response and consider alternative reactions based on awareness gained.
- Progress Documentation: Regularly review journal entries to observe trends, improvements, or recurring challenges. Recognizing progress boosts motivation and informs adjustments to mindfulness routines.
Maintaining Consistent Mindfulness Practices in Stressful Situations
Staying committed to mindfulness during stressful encounters can be challenging yet is vital for effective anger management. Preparing strategies beforehand ensures resilience and facilitates calm responses when anger arises unexpectedly.Tips include:
- Pre-Planning and Visualization: Visualize yourself handling stressful situations calmly and mindfully. Creating mental rehearsals prepares the mind for real-life application, reducing reactive tendencies.
- Carry Mindfulness Reminders: Use physical cues such as a bracelet, note, or breath anchor to prompt mindful awareness during tense moments. These cues serve as gentle reminders to pause and breathe.
- Pause and Breathe: Practice the “STOP” technique—Stop, Take a deep breath, Observe thoughts and feelings, and Proceed with awareness. Applying this simple step during stress prevents escalation and fosters composure.
- Develop a Stress-Response Plan: Artikel specific actions—like stepping away, practicing breathing exercises, or repeating affirmations—that can be quickly employed in stressful moments to regain center.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Meditation Practice
Engaging in meditation for anger management can present various obstacles that may hinder progress or diminish motivation. Recognizing these challenges and implementing effective strategies can significantly enhance your practice, leading to more consistent and beneficial outcomes. It is common for practitioners to encounter distractions, restless thoughts, or feelings of impatience, especially when starting out or during stressful periods. Developing resilience and adopting practical solutions are essential in overcoming these hurdles and maintaining a steady path toward emotional calmness and self-awareness.
Meditation, particularly in the context of anger management, requires patience, persistence, and adaptability. The process of calming the mind and reducing emotional reactivity involves navigating internal and external obstacles. Understanding the typical issues faced can empower you to address them proactively, ensuring that your meditation sessions remain productive and aligned with your emotional well-being goals.
Identifying Typical Obstacles in Meditation for Anger Management
Common challenges experienced during meditation to manage anger include difficulty maintaining focus, intrusive or restless thoughts, physical discomfort, and emotional resistance. New practitioners often find their minds wandering to everyday worries or past frustrations, which makes sustained concentration difficult. Restlessness, impatience, or a tendency to judge oneself negatively for not “doing it right” can also impede progress. Additionally, external distractions such as noise, interruptions, or uncomfortable environments can disrupt the meditative process.
Strategies to Stay Motivated and Committed to Regular Practice
Maintaining motivation for meditation involves establishing a consistent routine, setting realistic expectations, and recognizing incremental progress. Incorporate meditation into daily schedules by choosing specific times, such as mornings or evenings, which helps establish a habit. Setting clear, achievable goals, like dedicating five minutes initially and gradually increasing duration, can prevent feelings of overwhelmedness. Tracking progress through journaling or meditation logs can provide visible evidence of improvement, reinforcing commitment.
Reminding yourself of the benefits—such as reduced anger episodes, greater emotional resilience, and improved relationships—can serve as powerful motivators to continue practicing regularly.
Solutions for Dealing with Distractions and Restless Thoughts During Meditation
Distractions and restless thoughts are natural aspects of meditation, especially during the early stages. Developing specific techniques to manage these issues can enhance focus and relaxation:
“Acceptance of distractions as part of the process allows the mind to settle more naturally into calmness.”
- Gentle Acknowledgment: Recognize distractions without judgment and gently redirect attention to your breath, mantra, or chosen focal point.
- Use of Anchors: Employ anchors like breathing, body sensations, or visualizations to anchor your attention and reduce wandering thoughts.
- Creating a Conducive Environment: Choose a quiet, comfortable space free from interruptions, and use calming elements such as soft lighting or ambient sounds.
- Practicing Patience: Understand that restless thoughts will diminish over time with consistent practice, and avoid frustration when they arise.
Troubleshooting Steps to Enhance Focus and Relaxation
When facing persistent difficulties in maintaining focus or achieving relaxation, the following troubleshooting steps can be beneficial:
- Adjust Your Practice Environment: Minimize external noise, ensure comfortable seating, and eliminate potential interruptions before starting.
- Start with Short Sessions: Begin with brief sessions, such as 3-5 minutes, and gradually increase duration as your focus improves.
- Practice Deep Breathing Exercises: Incorporate diaphragmatic breathing to calm the nervous system and prepare the mind for meditation.
- Use Guided Meditations: Listening to structured guided sessions can provide direction and help maintain focus during practice.
- Address Physical Discomfort: Ensure your posture is comfortable and supportive to prevent physical distractions.
- Implement a Consistent Routine: Meditate at the same time daily to build habit and familiarity, which can reduce resistance.
- Be Compassionate with Yourself: Recognize that challenges are natural; avoid self-criticism and focus on gentle progress.
Regularly practicing these troubleshooting steps can transform obstacles into opportunities for growth, ultimately fostering a more peaceful and effective meditation experience for anger management.
Enhancing Meditation with Complementary Techniques

Meditation for anger management can be significantly more effective when paired with complementary practices that reinforce relaxation, awareness, and emotional regulation. Integrating physical activities, sensory elements, and mental reinforcement tools enriches the meditation experience, making it more sustainable and impactful in managing anger over the long term. These additional techniques support the development of a balanced mind and a calm demeanor, helping individuals respond to stressors with greater resilience and clarity.Combining meditation with other calming and centering methods creates a multi-faceted approach to anger management.
When these practices work together, they address physical tension, emotional triggers, and mental patterns comprehensively. This integration can deepen meditation benefits, improve emotional regulation, and foster a more harmonious state of mind.
Physical Activities like Yoga and Tai Chi
Engaging in gentle physical exercises such as yoga or tai chi complements meditation by releasing built-up tension and promoting bodily awareness. Both practices incorporate controlled breathing, mindful movements, and postures that align with meditative principles, fostering a holistic approach to stress reduction. For example, yoga sequences focused on calming poses, such as child’s pose or seated forward bends, help soothe the nervous system and prepare the mind for deeper meditation.
Similarly, tai chi’s slow, flowing movements enhance proprioception and emotional regulation, making it easier to maintain calmness during meditation sessions. Incorporating these practices into an anger management routine creates a synergy where physical and mental relaxation reinforce each other.
Use of Calming Music and Ambient Sounds
The auditory environment plays a crucial role in shaping the meditation experience. Calming music, nature sounds, or ambient soundscapes serve to mask distracting noise and create a serene atmosphere conducive to relaxation. Soft instrumental music, such as gentle piano or flute melodies, can help slow the heart rate and deepen meditative focus. Nature sounds like flowing water, ocean waves, or bird calls evoke feelings of tranquility and connection to the environment.
These auditory elements can be embedded within meditation sessions, helping individuals maintain focus, reduce mental chatter, and foster a peaceful state conducive to anger alleviation.
Breathing Aids and Affirmations
Breathing aids, such as guided breathing exercises or portable devices that provide visual or tactile cues, support the development of steady, calming breaths essential for anger control. Affirmations—positive, reinforcing statements—can be integrated into meditation to strengthen mental resilience. Repeating affirmations like “I am calm,” “I release anger,” or “I am in control” during meditation sessions helps reprogram negative thought patterns and reinforce feelings of composure.
These tools serve as mental anchors, providing additional support when emotional turbulence arises, and help solidify the benefits gained through meditation.
Supplementary Practices Supporting Anger Management
| Practice | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Progressive Muscle Relaxation | Systematically tensing and relaxing muscle groups to reduce physical tension and promote relaxation. | Reduces bodily tension associated with anger, making it easier to stay calm during meditation. |
| Mindful Walking | Walking slowly in a quiet environment while paying close attention to each step and breath. | Enhances awareness and reduces impulsive reactions, supporting emotional regulation. |
| Journaling | Writing down feelings, triggers, and reflections to process emotions consciously. | Facilitates emotional clarity and decreases the likelihood of anger outbursts. |
| Biofeedback | Using electronic monitoring to gain awareness and control over physiological functions like heart rate. | Helps individuals learn to regulate physiological responses associated with anger. |
Final Wrap-Up
Incorporating meditation into your daily routine offers a sustainable and effective way to manage anger and cultivate emotional resilience. By exploring different techniques and staying committed to regular practice, you can experience lasting benefits that improve your mental health and overall quality of life. Remember, patience and consistency are key in mastering the art of meditation for anger management.